How LCAs for Water Bottles Work
This video explains the life cycle analysis (LCA) of water bottles, focusing on the three main phases: production, use, and end-of-life.
Key moments with timestamps:
- 0:00-1:00: Introduction to LCA and the three phases for water bottles.
- 1:00-2:30: Breakdown of the production phase, highlighting its significant impact and various data inputs like resource extraction, manufacturing, packaging, and beverage production.
- 2:30-3:30: Explanation of the use phase for single-use water bottles, including transportation, washing, and refrigeration.
- 3:30-4:30: Comparison of the use phase for single-use and reusable water bottles, emphasizing the longer use cycle and additional washing factor for reusables.
- 4:30-5:30: Discussion of the end-of-life phase and its dependence on disposal methods like recycling or landfilling.
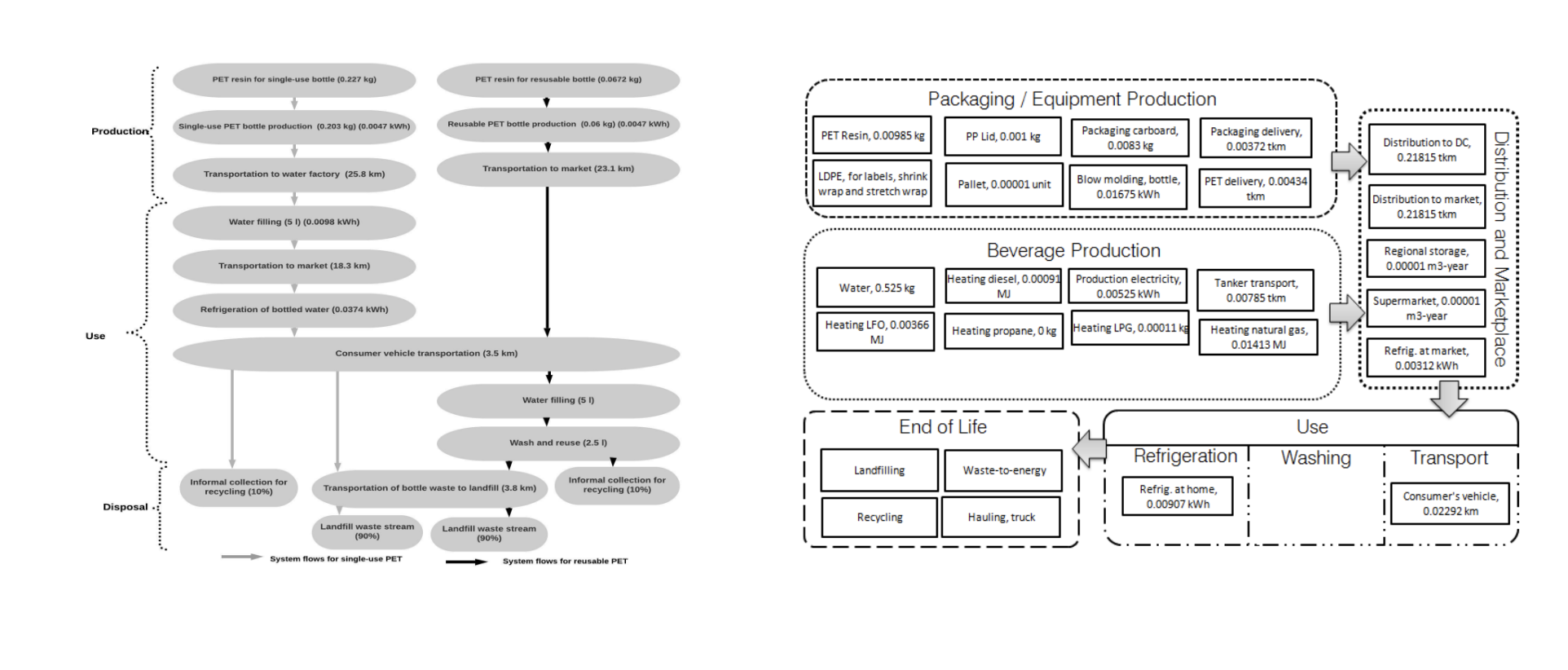
- 5:30-6:30: Comparison of the life cycle of single-use and reusable water bottles using a diagram, showcasing the significant impact of the production phase for both.
Additional details:
- The video mentions that most of the impact for water bottles comes from the production phase.
- The use phase for single-use water bottles is relatively low compared to production.
- The life cycle analysis of reusable water bottles includes factors like the number of uses and the source of water.
- Different studies may have different assumptions and scenarios, leading to variations in the results.
Data Sources
[1] Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Drinking Water Alternatives and Consumer Beverage Consumption in North America (Access)
[2] Life cycle assessment of single-use and reusable plastic bottles in the city of Johannesburg (Access)
Olatayo KI, Mativenga PT, Marnewick AL. Life cycle assessment of single-use and reusable plastic bottles in the city of Johannesburg. S Afr J Sci. 2021;117(11/12), Art. #8908. https://doi.org/10.17159/ sajs.2021/8908
[3] Reusable vs Single-Use Packaging: A Review of Environmental Impacts (Access)