Air Date: Week of November 5, 2021
stream/download this segment as an MP3 file
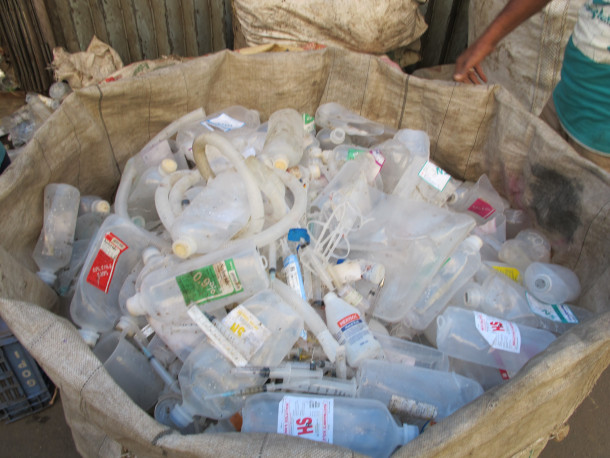
Some cement factories are collecting plastic waste from consumer goods businesses and landfills to use as fuel to fire their kilns, posing the risk of polluting air with toxic chemicals. (Photo: Xopolino on Wikimedia Commons)
This week, Host Bobby Bascomb talks with Peter Dykstra, an editor at Environmental Health News, about the public health hazards of cement kilns burning plastic waste as a source of fuel. And in California, Scripps Institution of Oceanography is building a 32,000-gallon simulated ocean to study the effects of climate change. Also, a trip back in time to November 1492 when native peoples introduced Christopher Columbus and his expedition to maize, which became a major food staple across the globe.
Transcript
BASCOMB: It’s time for a trip now Beyond the Headlines with Peter Dykstra. Peter’s an editor with Environmental Health News, that’s ehn.org, and DailyClimate.org. Hey there, Peter, what do you have for us this week?
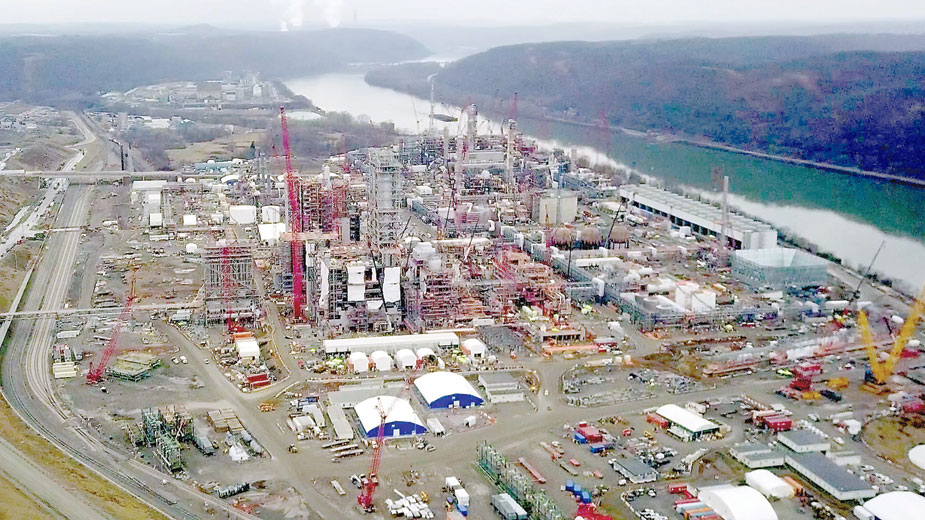
DYKSTRA: Hi, Bobby. There’s an investigative story from Reuters. They’ve looked into cement kilns, cement kilns are everywhere, especially in booming cities in the developing world. They’re responsible for 7% of all the greenhouse gases emitted. So that’s a huge chunk. And right now, those cement kilns are looking for a new source of fuel to fire up the kilns and they’ve hit upon plastic waste. And that can be a bigger problem than any problem they may be solving.
BASCOMB: Hmm. Well, that makes sense. I mean, plastic is made with fossil fuels. So it’s, you know, pretty energy rich and there’s so much plastic waste out there. It’s free, or maybe even in some places might pay to have it, you know, burned like that. But of course, you know, it’s not too good for air quality now, is it?
DYKSTRA: Right, and there are consumer firms that are funding projects to send their plastic trash to cement plants. It’s a dangerous idea, given the amount of carcinogenic fumes that exists in those plastics, now burning straight, from, in many cases, the developed world to the developing world, to all of our lungs.
Cement factories are burning plastic to fire up massive cement kilns like the one pictured here. (Photo: LinguisticDemographer on Wikimedia Commons)
BASCOMB: Yeah, I mean, looking at things like dioxins, heavy metals, carcinogens. I mean, it’s pretty, pretty toxic stuff.
DYKSTRA: And it’s been said that burning plastics in cement kilns doesn’t help lessen the landfill problem. It simply transfers the landfills from being on the ground to in the skies.
BASCOMB: Well, that certainly is a big problem. Well, what else do you have for us this week Peter?
DYKSTRA: It’s kind of a weird sci-fi sort of project. The Scripps Institute out in San Diego is building a 32,000 gallon tank that has a wind tunnel on top of it. And with all that, they hope to synthesize what happens in the ocean, and how the oceans can affect climate change.
BASCOMB: How will they do that?
DYKSTRA: There are wind currents brought in, water currents introduced mechanically into this tank, and we’ll see what happens as climate change begins to alter both wind and wave and current patterns. It’ll give a little bit more of an insight as to what lies ahead in our future, as climate change really takes hold in our oceans.
The surface layer of the ocean can tell scientists a lot when looking at climate change. That is one aspect researchers at Scripps Institution of Oceanography will study in their simulated ocean. (Photo: NOAA on Wikimedia Commons)
BASCOMB: So they can simulate climate change in this pool and sort of speculate what we’re going to be looking at then.
DYKSTRA: Right, and thanks for using the word pool because 32,000 gallons sounds like a lot, but it’s actually about 5% of what it takes to fill in a competition sized Olympic swimming pool.
BASCOMB: So it’s really not all that big then. It’s amazing what they can do in such a small space.
DYKSTRA: It is. Scientists can have fun with it and can give us some information that’ll help guide us through a particularly dangerous time in our environmental future.
BASCOMB: Indeed, well, what do you have for us from the history books this week?
DYKSTRA: November 5, 1492. And we all know what happened in 1492. Columbus sailed the ocean blue. And on his subsequent stop to the Bahamas, Columbus went to Cuba in early November, and he was introduced to maize. That corn was brought back to Europe and has since become a global staple for both humans and livestock.
BASCOMB: Well, yeah, there’s so much to that. I mean, that the Columbian Exchange brought tomatoes and potatoes to Europe. I mean, imagine Italian food without tomatoes, but before that, they made do I guess.
Maize has become a food staple around the world after it was introduced from the New World to the Old World in 1492. (Photo: Balaram Mahalder on Wikimedia Commons)
DYKSTRA: And even though Columbus was a tip of the spear, coming from Europe, in the genocide of native peoples in the West, one other thing that was a gift so to speak, from North America to Europe was of course, tobacco. So it’s feed ya and kill ya, Mr. Columbus.
BASCOMB: All right. Well, thanks Peter. Peter Dykstra is an editor with Environmental Health News. That’s ehn.org and DailyClimate.org. We’ll talk to you again real soon.
DYKSTRA: Okay, Bobby. Thanks a lot. Talk to you soon.
BASCOMB: And there’s more on these stories on the Living on Earth website. That’s loe dot org.
Links
Reuters | “Trash and Burn: Big Brands Stoke Cement Kilns with Plastic Waste as Recycling Falters” WIRED | “This Groundbreaking Simulator Generates A Huge Indoor Ocean” Read more about the Columbian Exchange