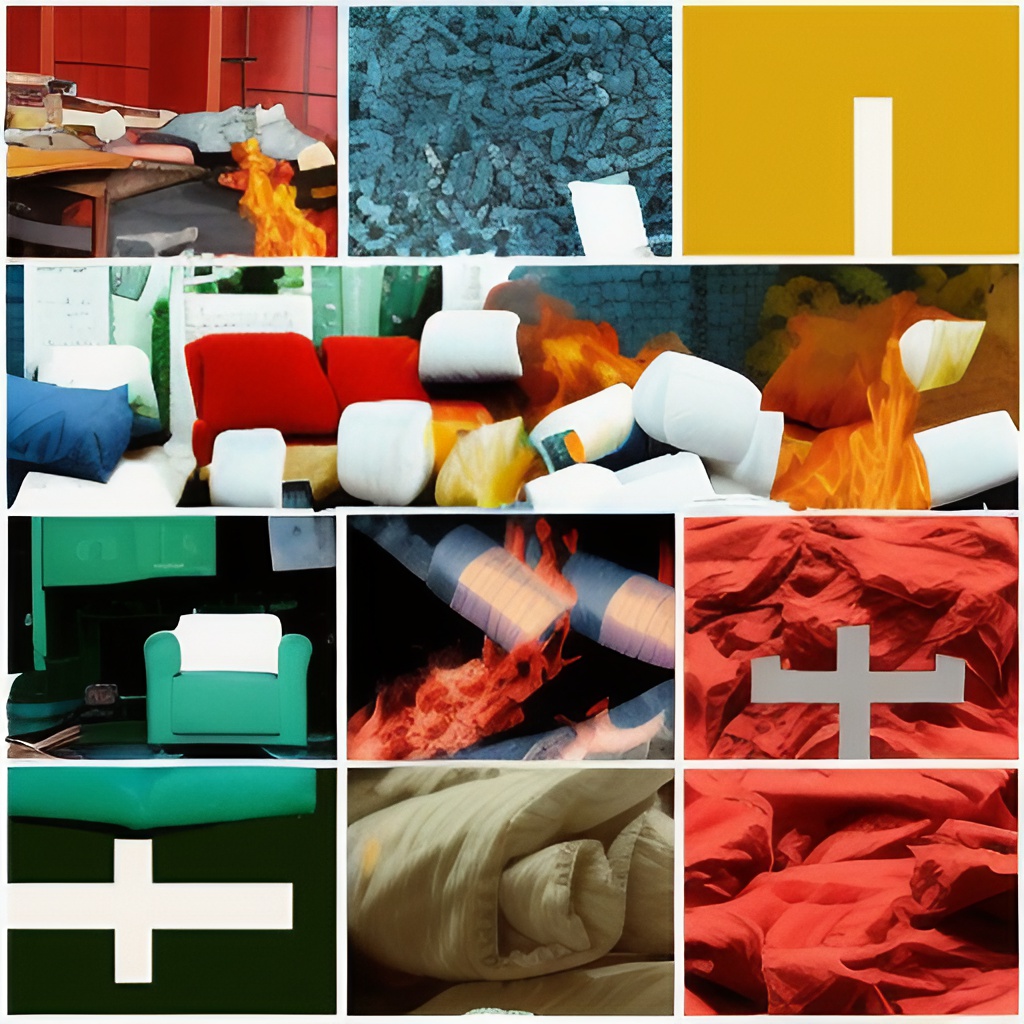
What Are Flame Retardants?
Flame retardants are chemicals used to slow down the spread of flame and delay the ignition of combustible materials. They can be found in a variety of products such as furniture, electronics, carpets, and flame-resistant plastics. While flame retardants can provide a measure of safety in preventing fires from occurring, their potential detrimental effects on human health have become an area of increasing concern for researchers.
Many flame retardants have been linked to lowered IQs, birth defects, reproductive issues, nerve damage, and hormone disruption. Given these potential risks, it is recommended that people be aware of flame retardant chemical usage in items they come into contact with on a daily basis and take measures to minimize exposure when possible.
How Are Flame Retardants Regulated?
Government regulation of flame retardants chemicals has been present since the 1970s, when successive waves of flame retardant products were being launched in the United States and Europe. The flame retardants used during this period contained polybrominated biphenyl (PBB) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), both of which have since been determined to cause serious risks to human health, including cancer, thyroid and fertility issues. As a result, production of these flame retardants was halted in 2004 due to investigations by the Environmental Protection Agency identifying their health hazards.
Newer flame retardant chemicals are now monitored for volatility and are regulated for environmental friendliness, flame-retardancy and low toxicity levels. To this end, policy makers continue to collaborate with industry leaders in order to maintain safe flame retardant regulation standards.
Europe: Highly Regulated
In the EU, flame retardants have been subject to regulation since the late 1970s, when there became greater awareness about the potential risks posed to human health. Over the last 40 years, regulations have evolved significantly and flame retardant chemicals are now subject to very stringent standards.
In recent years, particular attention has been given to ensure flame retardants are used in a safe and controlled manner within products coming into contact with humans. This has seen flame retardant substances banned in certain applications such as toys or nursery items being placed on the market by EU countries in order to protect children’s safety.
United States: Regulated
In the United States, flame retardant chemicals are regulated by the Consumer Product Safety Commission which enforces standards that flame retardants must adhere to in order to be deemed safe for public use. Flame retardant manufacturers must file a report describing their products which includes details regarding what their product contains as well as how it works. These regulations help protect against the most toxic and most studied flame retardants, but don’t capture all chemicals within this family.
Canada: Regulated
Canada has taken several steps to protect its citizens from potentially harmful flame retardants. Most notably, in 2011, amendments to the Canadian Environmental Protection Act banned flame retardants in any polyurethane foam and other product materials found in baby furniture, car seats, and other consumer items accessed by children.