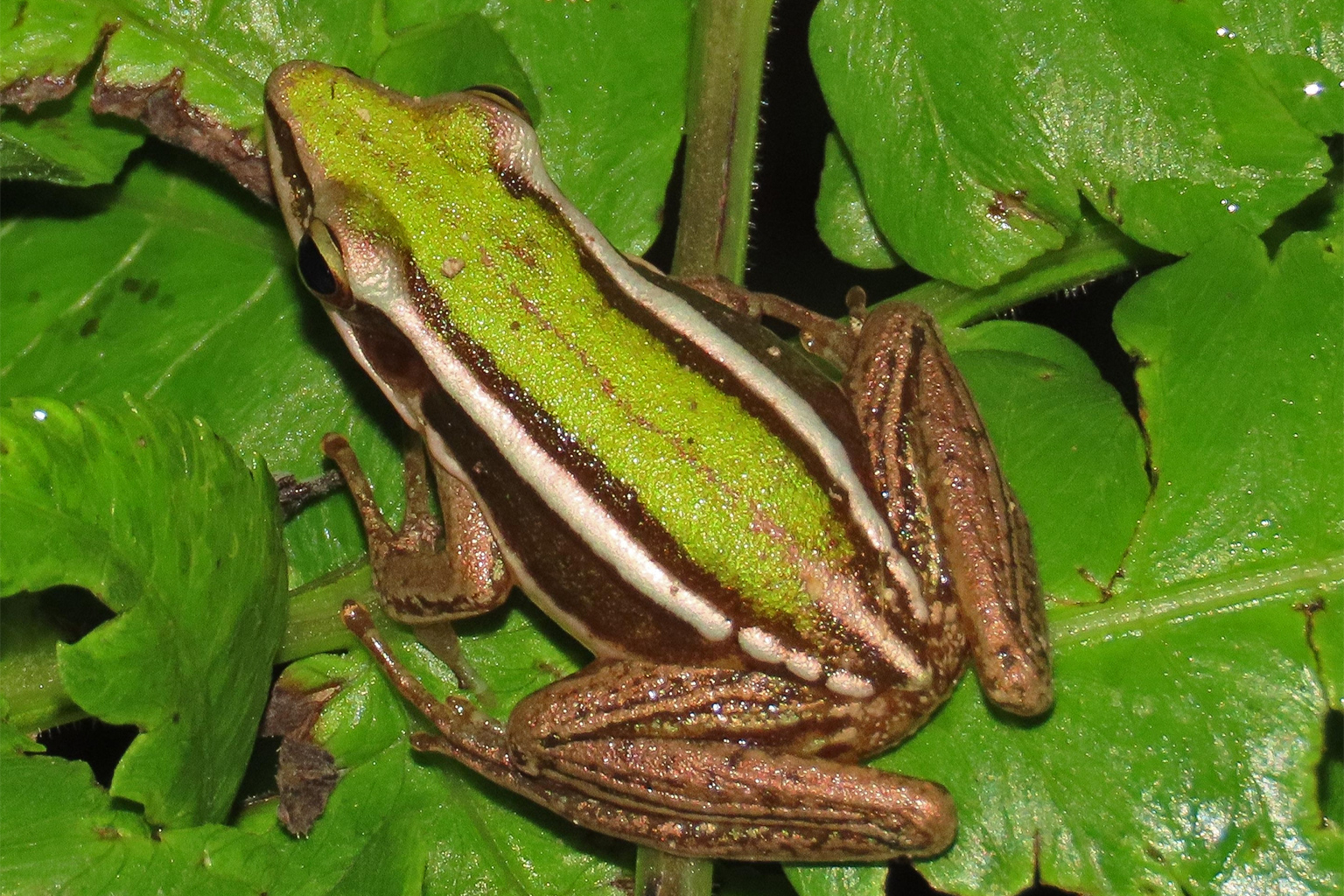
A new study has found that shorttail fanskate populations may be being affected by plastic pollution.The skates mistake abandoned fishing nets and other debris for seaweed and attach their eggs to them, unaware that the debris could wash up on the shore where the eggs will dry out.Shorttail fanskates (Sympterygia brevicaudata) are considered near threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). In recent decades, plastic pollution has become a key environmental issue. An estimated 8 million metric tons of plastic waste enter the ocean each year, equivalent to a truckload of garbage dumped into the sea every minute — and it’s only projected to get worse. Scientists have reported that numerous marine species mistake plastic for food and ingest it, or become trapped in garbage, both of which can seriously threaten their survival. In addition, invertebrates and other marine organisms can become attached to floating plastic that travels long distances around the world, and scientists have warned that they risk becoming invasive alien species in their final destinations.
An iguana eating a plastic bag. Image courtesy of Galapagos Science Center.
A new study has revealed another problem with marine garbage, one that could be endangering Peru’s populations of shorttail fanskates (Sympterygia brevicaudata), a species of skate that is already considered near threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The study’s authors report that it is common to see dead, dried-up skate egg cases attached to marine garbage washed up on beaches. The study was published in June in the journal Marine Pollution Bulletin.
But how do the eggs get caught in marine debris, and why do they die?
Hundreds of dead egg cases entangled in marine debris
In the city of Trujillo in northern Peru, members of the NGO ConservAccion conduct a survey of animals that, for various reasons, wash up on the area’s beaches. They’ve noticed that it it’s common to see skate egg cases attached to marine debris and that, most of the time the eggs have dried out, dooming the baby skates inside. Wanting to find out how widespread the problem is, the experts set themselves the task of counting all the eggs, identifying the type of garbage and plastic, and determining the places where this is most common.
“They are like little bags,” is how veterinarian Carlos Calvo-Mac, ConservAccion’s project director, described shorttail fanskate egg cases. “They are usually called mermaid’s purses, because they have that shape and even a leather-like texture,” he said.
Shorttail fanskate egg cases, photographed near Puerto Morín, Peru. Image by rob-westerduijn via iNaturalist (CC BY-NC 4.0).
“Skates do not give parental care; they simply lay their eggs,” said Miguel Valderrama Herrera, a fisheries biologist with ConservAccion and the study’s lead author. They make sure the eggs are fixed to something to prevent them from floating away. To enable this, the eggs have a tendril, “like a little rope that lets them attach, for example to algae,” he said.
In tropical seas, skates often attach the egg cases to coral, but they can use any structure, Valderrama said. This is how shorttail fanskates sometimes unwittingly choose marine debris, such as nets or other types of plastic, to deposit their egg cases. “What they don’t know is that these things, due to the action of the tide, can end up beached,” the biologist said. When it remains out of the water, the egg case dries out before it can hatch, and it dies.
During the shorttail fanskate’s spawning season between February and April, a group of eight people, made up of experts and volunteers, visited three beaches in the region of La Libertad, on the northern coast of Peru. They were looking for clusters of marine debris that had been in the sea for a certain period of time, to determine whether they contained egg cases.
Dried shorttail fanskate egg cases, which turn black when they dry, caught in marine debris. Image courtesy of ConservAccion.
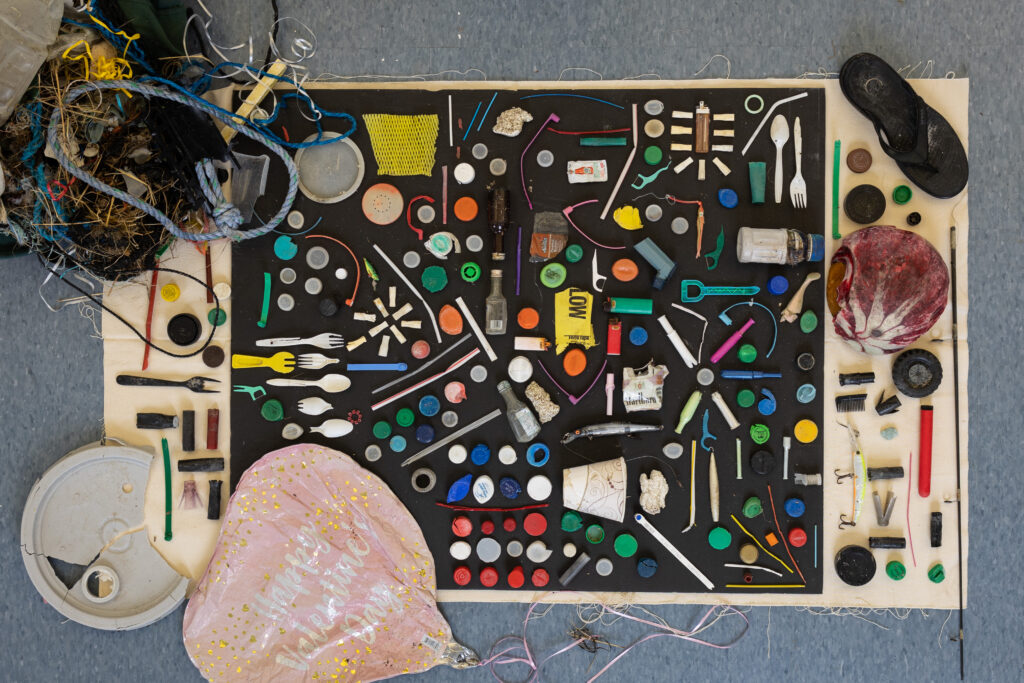
In total, the researchers recorded 75 clusters containing 1,595 egg cases. Of these, 15.9% had presumably hatched. And of the total, 15.8% were still fresh, but the rest, 84.2%, had dried out.
The waste itself was mainly composed of plastic associated with fishing materials, primarily nets used by artisanal fishers. “These nets, made up of … a series of holes, are a tempting place for the skates to attach their eggs. The way they move in the water, being so light, can also imitate the movement of algae,” Valderrama said. Less frequently, the egg cases were also attached to fabric, rubber, foam plastic, metal, wood, paper or cardboard.
Most of the debris clusters and egg cases were found in the vicinity of the town of Puerto Morín, followed by the town of Salaverry and city of Huanchaco, according to the study. Valderrama said there were two reasons why most of the dried eggs were found in clumps of waste around Puerto Morín. “Puerto Morín survives almost exclusively from fishing and, being a bay, the clusters easily get trapped,” he said. The large number of egg cases found there have also led researchers to believe it may be a spawning ground for shorttail fanskates.
How much does the loss of all these eggs affect the shorttail fanskate’s survival?
Researchers analyze waste clusters while looking for shorttail fanskate egg cases. Image courtesy of ConservAccion.
A vulnerable species
Shorttail fanskates are typical of the shallow waters of the southeastern Pacific along the coasts of Ecuador, Peru and central Chile. They inhabit depths of 8-100 meters (26-328 feet), although they have also been accidentally caught by crustacean fisheries operating at depths down to 500 meters (1,640 feet), according to the study.
Even though fishers do not intentionally target fanskates, they are categorized as near threatened by the IUCN. Like sharks and chimaeras, skates are among the most threatened marine animals. In 2021, scientists classified one-third of the world’s species of sharks, rays, skates and chimaeras — 391 out of 1,199 species evaluated— as being critically endangered, endangered or vulnerable according to the IUCN. Species in these three IUCN categories are considered to be threatened with extinction.
In addition to being accidentally captured by nets and hooks set for other species, these animals “reproduce very little, so when they are affected by fishing or pollution, it can be very harmful,” Valderrama said.
A shorttail fanskate (Sympterygia brevicaudata). Image by ulrichzanabria via iNaturalist (CC BY-NC 4.0).
“Although there are numerous initiatives aimed at cleaning up solid waste on Peru’s beaches, I have yet to see any study on the impact of these campaigns. Do they really help?” said Calvo-Mac. According to the study’s authors, there’s a possibility WWF-Peru might install a fishing net recycling point in Puerto Morín.
WWF-Peru and Bureo, a fishing-gear recycling company, have already set up collection points in other areas along the Peruvian coast where fishermen can leave nets they no longer use and can learn about the impact of abandoning nets at sea. One of these points is on Los Organos beach, also located in the north of the country. “We saw truly great results just by offering this information and somewhere to deposit old nets,” said Aimée Leslie, WWF-Peru’s conservation director.
Banner Image: A washed-up egg case of a shorttail fanskate. Image by ulises_inf via iNaturalist (CC BY-NC 4.0).
This story was first reported by Mongabay’s Latam team and published here on our Latam site on May 24, 2023.
Seeking a sanctuary for Peru’s sea life: Q&A with Yuri Hooker
Citations:
Avila, C., Angulo-Preckler, C., Martín-Martín, R. P., Figuerola, B., Griffiths, H. J., & Waller, C. L. (2020). Invasive marine species discovered on non–native kelp rafts in the warmest Antarctic island. Scientific Reports, 10(1). doi:10.1038/s41598-020-58561-y
Valderrama-Herrera, M., Cardenas, S. A., Calvo-Mac, C., Celi-Vértiz, R. G., Chumpitaz-Levano, V. L., Flores-Miranda, W. E., … De-la-Torre, G. E. (2023). Rajids ovipositing on marine litter: A potential threat to their survival. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 191, 114941. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.114941
Dulvy, N. K., Pacoureau, N., Rigby, C. L., Pollom, R. A., Jabado, R. W., Ebert, D. A., … Simpfendorfer, C. A. (2021). Overfishing drives over one-third of all sharks and rays toward a global extinction crisis. Current Biology, 31(22), 5118-5119. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2021.11.008
Animals, Biodiversity, Coastal Ecosystems, Conservation, Fish, Marine Animals, Marine Biodiversity, Marine Conservation, Marine Protected Areas, Oceans, Plastic, Pollution, Protected Areas, Rays, Sharks And Rays, Wildlife
Print