How is my exposure to plastics impacting my health? This is a question I’ve had for a long time… a question that various blogs and articles I’ve read attempted to answer but never covered to my satisfaction. So I did the research to find out for myself.
While my suspicions were validated in some areas, in others I was surprised with what I found. Here are the answers I’ve found through my research.
TLDR: The Executive Summary
What potentially harmful chemicals does plastic expose us to?
There are 63 known chemicals associated with plastic packaging that are classified as “most hazardous” by the United Nations’ GHS (Global Harmonized System).
When a chemical is classified under GHS as “most hazardous,” particularly in the context of health hazards, it implies that it falls into the highest severity category for one or more of their health hazard criteria. This might include being a known or presumed carcinogen, having high acute toxicity (can cause adverse health effects from short-term exposure), or being a known reproductive toxin, among other criteria.
Plastic packaging is an important category to look at because for most of us it accounts for our highest exposure to plastics. In addition to the 63 most hazardous chemicals, there are:
- 906 chemicals likely associated with plastic packaging
- 3,377 chemicals associated with plastics and possibly associated with packaging
Takeaway: There are a lot of chemicals that are known to be hazardous to our health and many more we don’t yet know much about.
Research Summary: Overview of Known Plastic Packaging Associated Chemicals and Their Hazards
What are the biggest sources of chemical exposure from plastics?
We are exposed to a variety of sources in many different ways. For most of us, these are the top exposure points:
- Plastic packaging – food, beverages, and products
- Appliances
- Microplastics in the environment – in our food chain through seafood, meat, fruits, vegetables, and drinking water, and even in the air
- Synthetic textiles
In addition, increasing amounts of microplastics are being found in the food chain [1], showing up in seafood, meat, fruits, and vegetables. They can also enter our drinking water [2] through pipes and treatment processes, and are even found in the air [3].
[1] Research Summary: Microplastics in the Food Chain
[2] Research Summary: Microplastics in Drinking Water
[3] Research Summary: Microplastics in the Air
How can I reduce my exposure?
The more I learn about plastics the more I try to reduce my exposure to them. You can significantly reduce your exposure to chemicals from plastics in three key ways:
- Reduce your use of plastics (My Guide)
- Be careful about the types of plastics you use
- Adjust the way you use plastics
The Details
Why have I compiled this research?
Problem #1: Regulatory bodies do not move fast enough to protect us. While it would be great to be able to rely on the government to do this research and pass legislation on our behalf… our system is too slow and entangled with special interests. I believe we need to be our own health advocates. Here’s why…
- How long did it take for cigarettes to be regulated?
- What are the government recommendations for a “healthy” diet?
- What regulations are there around Social Media and it’s impact on mental health?
Problem #2: Everyone has an opinion. We hear a lot of anecdotal stories and read a lot of catchy headlines that can skew our perception on this topic. I don’t want to make big lifestyle decisions (like avoiding plastic) based on faulty information.
Problem #3: There’s still a lot of unknowns. There are so many types of plastics, additives, and use cases that haven’t been thoroughly researched yet. This is due to a combination of the sheer volume, lack of funding, and the amount of time required to run proper experiments. While it would be prudent to just steer clear of plastics altogether, in practice it’s very difficult to do without completely withdrawing from modern society.
Very few people have the time to review what the experts are saying in detail. Even fewer can actually go to the source and review the peer-reviewed literature. Since I’ve taken the time to do this for myself, I’ve made the extra effort to publish it so hopefully I can save you some time too.
Here’s what I’ve found:
Plastic’s Effect On Our Body
How can plastic particles and chemicals get into our body?
Plastics and the chemicals associated with them get into our body primarily through ingestion. On a daily basis most of us are consuming various forms of microplastics, nanoplastics, plastic molecules, and a host of chemicals that are along for the ride through the food we eat and beverages we drink. On a much smaller scale we can also inhale plastic-related particles and there is potential for some chemicals associated with plastics to be absorbed through the skin.
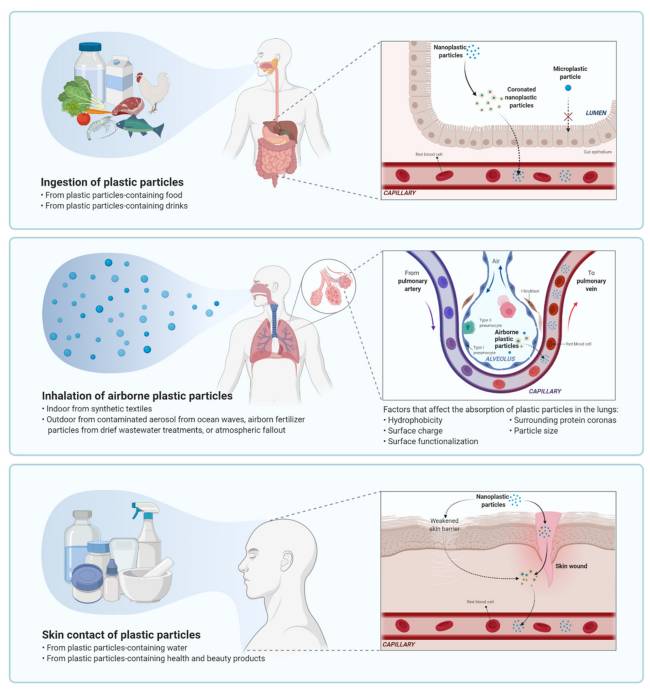
The effect these substances have on our body depends on several factors, mainly:
- Size
- Quantity
- Toxicity
Size Review: Microplastics, Nanoplastics, and Plastic Molecules
Understanding the size classifications for plastic particles is helpful because some size ranges are small enough to pass into the cells of our body where they may have adverse effects.
Plastic > Microplastic > Nanoplastics > Polymer > Monomer > Molecule
Microplastics: Tiny pieces of plastic, typically less than 5 millimeters in size. They can be primary microplastics, designed to be small for use in products like cosmetics or industrial abrasives, or secondary microplastics, resulting from the breakdown of larger plastic items due to environmental factors like sunlight, wave action, or mechanical stress.
Nanoplastics: Nanoplastics are much smaller, typically less than 100 nanometers in size (0.0001 millimeters). Microplastics are classified as up to 5,000,000 nm and nanoplastics up to 100 nm. Nanoplastics can form from the further breakdown of microplastics or be released directly into the environment from various sources.
Polymers: Plastics are composed of long chains of molecules known as polymers, which are made from repeating units of monomers. These molecules are on a molecular scale, much smaller than microplastics, and are not visible to the naked eye.
Monomers: A monomer is a molecule that can react with other identical or different molecules to form a polymer. These basic building blocks are typically small, simple molecules with the capacity to link together through chemical bonds, often in long chains.
Molecules: A molecule is a group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction. Molecules are composed of two or more atoms, which can be the same (as in O2, which is oxygen) or different (as in H2O, which is water).
Chemicals: A chemical, by definition, is simply a group of molecules. Water is a chemical, composed of hydrogen and oxygen. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) are examples of more complex chemicals used in common plastics like bottles and pipes. These are longer chains of molecules forming polymers. Bisphenol A (BPA) is also a chemical; it is commonly used as an additive to plastics. BPA and other additives are used to adapt plastics to meet their use case – making them softer, more flexible, clearer, flame resistant, etc.
Colloquially, we use the term “chemicals” to mean molecules like BPA that are additives to the main plastic polymer.
What can get into our bloodstream?
Certain chemicals from plastics can enter the human bloodstream. Examples include:
- Micro and nanoplastics – in 2022 researchers found particles of the size 700 nanometers (nm) and larger in the bloodstream (microplastics typically range in size from 1,000 nm to less than 5,000,000 nm; nanoplastics are typically defined as less than 100 nm) [1]
- Polymers and monomers – particles found in the same study included polymers;
- Chemical additives – it is well documented that chemical additives commonly found in plastics such, as BPA and phthalates, can enter the bloodstream.
To get into our bloodstream chemicals need to be able to pass through the gastrointestinal barrier in our gut.
The passage of chemicals through the gastrointestinal barrier is influenced by several factors:
- Molecular Size: Larger molecules often have difficulty passing through the barrier.
- Solubility: Lipid-soluble substances pass through more easily than water-soluble ones.
- Chemical Structure: Certain structures may be more easily absorbed.
- Concentration Gradient: Higher concentrations outside the gut may promote absorption.
- Intestinal pH: This affects the ionization of substances, influencing absorption.
- Gut Microbiota: Can metabolize or interact with chemicals.
- Integrity of the Barrier: Damage or inflammation can increase permeability.
These factors work together to regulate the absorption of nutrients and prevent harmful substances from entering the bloodstream.
[1] Research Summary: Plastic Particles in Human Blood
[2] Research Summary: Impact of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Human Health
Key Takeaway: Research shows that various types of chemicals from plastics can enter our bloodstream.
What plastic particles can get into our tissues or cells?
Plastic particles can enter our cells and build up in our tissues. There is still much to learn about the extent to which this happens and the impact it has on us.
Our Tissues – A study in July 2023 found microplastics in the heart and surrounding tissues [1].
Our Cells – Multiple studies have demonstrated that plastic particles can enter and interact with human cells [2]. Cellular uptake of nanoparticles is well documented; [3].
[1] Research Summary: Microplastics in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery
[2] Review Summary: Potential Toxic Effects of Nanoplastics on Human Health
[3] Review Summary: Cellular Uptake of Nanoparticles
What impact can this have on our health?
Various research studies have documented the toxic effects plastic particles can have on animal cells and human cells. The known short-term impacts include inflammation, cell damage, and metabolic disruption in cells. Many of these studies have been conducted in vitro (cell cultures outside of the body) or in mice.
More Info: Summary of potential toxic effects of micro- and nanoplastics on human health
The full extent of how plastic particles in our body impact our health is not likely to be known for a long time, but research is continuing to provide more insights each year.
Additives: Toxic Chemicals Associated with Plastics
What toxic chemicals are associated with plastics?
The most well-known chemicals associated with plastic include these families:
- Bisphenols – BPA, BPS, BPF
- PFAS – known as “forever chemicals”
- Phthalates – found in a wide range of plastic consumer products
- Flame Retardants – used to reduce flash point of products
- PCBs – mostly found in older appliances with plastic components
- Parabens – widely recognized as a risk in cosmetics, but also associated with plastics
- Azo Dyes – used primarily in textiles (synthetic and natural), and colored plastics
There are a considerable number of additional chemical families associated with plastic that are lesser known, but are still classified as hazardous or toxic. Explore the full list of classified hazardous chemicals here.
Research Summary: Overview of Known Plastic Packaging Associated Chemicals and Their Hazards
What impact can exposure to these chemicals have on our health?
Several families of chemicals associated with plastics are known to have negative health implications. The largest class of these chemicals is known as Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs). EDCs are of particular concern because they disrupt our body’s hormones and can lead to cancer, metabolic disorders, reproductive problems, and much more. [1]
These EDCs are the most well-known plastic additives commonly found in plastic packaging and home appliances:
- Bisphenols
- Phthalates
- Heavy Metals
- Flame Retardants
[1] Research Summary: Potential Effects of Additives of Concern on Human Health
Safe Exposure Levels: What amounts of plastic particles or associated chemicals is too much?
It is unclear if there is a safe level of exposure to plastic particles or associated chemicals. Determining safe exposure levels for chemicals is complex for multiple reasons [1]:
- Numerous chemicals, including EDCs, have documented effects at low doses that do not cause overt toxicity but are associated with significant health outcomes.
- Historically, as new data has been evaluated, “safe levels” for substances have been lowered. This produces uncertainty on whether current “safe levels” are accurate.
- Health implications vary widely from person to person based on sensitivity. Sensitivity includes many variables such as genetic makeup, lifestage, and combined environmental factors.
Experts in the field commonly give this advice:
- Reduce exposure when possible
- Be particularly cautious in developmental states as these populations are more sensitive: during pregnancy, infants, and adolescents
[1] Thresholds and Endocrine Disruptors: An Endocrine Society Policy Perspective
Guides & Resources
My Guide: How I Keep My Plastic Exposure Low
Harmful Chemicals Found in Plastics
Research: Plastics & Reproductive Health
Related Topics
Still Have Questions?
You can submit a question here and I’ll see if I can get you answers.